mygrad.nnet.activations.hard_tanh#
- mygrad.nnet.activations.hard_tanh(x: ArrayLike, *, lower_bound: Real = -1, upper_bound: Real = 1, constant: bool | None = None) Tensor[source]#
Returns the hard hyperbolic tangent function.
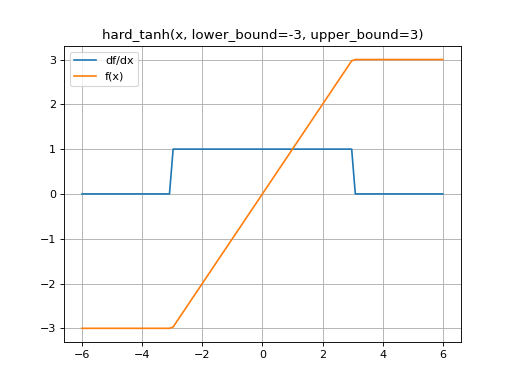
The hard_tanh function is lower_bound where x <= lower_bound, upper_bound where x >= upper_bound, and x where lower_bound < x < upper_bound.
- Parameters:
- xArrayLike
The input, to which to apply the hard tanh function.
- lower_boundReal, optional (default=-1)
The lower bound on the hard tanh.
- upper_boundReal, optional (default=1)
The upper bound on the hard tanh.
- constantOptional[bool]
If
True, the returned tensor is a constant (it does not back-propagate a gradient).
- Returns:
- mygrad.Tensor
The result of applying the “hard-tanh” function elementwise to x.
Examples
>>> import mygrad as mg >>> from mygrad.nnet.activations import hard_tanh >>> x = mg.arange(-5, 6) >>> x Tensor([-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) >>> y = hard_tanh(x, lower_bound=-3, upper_bound=3); y Tensor([-3, -3, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3]) >>> y.backward() >>> x.grad array([0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0.])
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)